Abstract
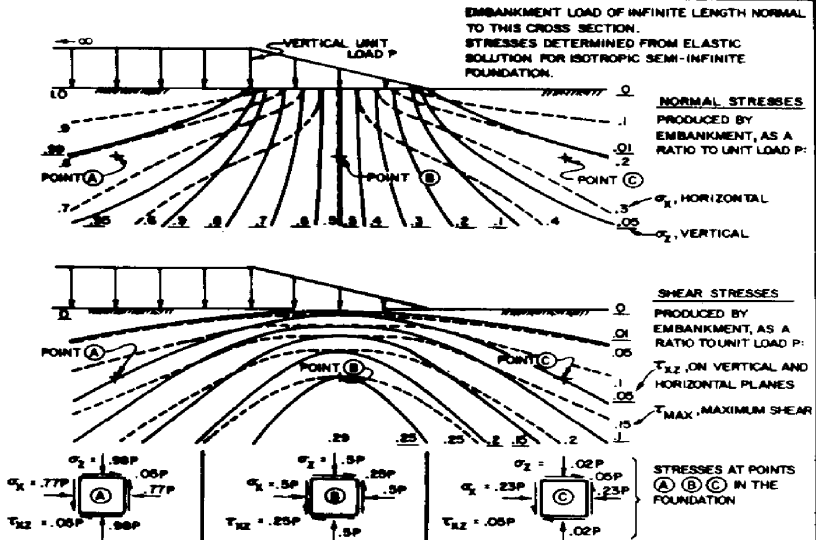
Mohr’s Circle-or more generally the stress equilibrium in solids-is a well known method to analyse the stress state of a two- or three-dimensional solid. Most engineers are exposed to its derivation using ordinary algebra, especially as it relates to the determination of principal stresses and invariants for comparison with failure criteria. In this presentation, an approach using linear algebra will be set forth, which is interesting not only from the standpoint of the stress state but from linear algebra considerations, as the problem makes an excellent illustration of linear algebra concepts from a real geometric system. A numerical implementation of the solution using Danilevsky’s Method will be detailed.
Download Mohr’s Circle Analysis Using Linear Algebra and Numerical Methods
Update: the online routine, which was the progression past the FORTRAN routine shown here, is being phased out. You can see this routine in spreadsheet form here, where there is also a link to the updated monograph. Other improvements to this routine are documented here as well.